
Specialty Equipment
Entrained Sulfur Removal Elements – Heated ESRE™
The Sulfur Condenser is a critical component of every Sulfur Recovery Unit. When properly designed, a condenser forms nice large drops of liquid sulfur that easily disengage in adequately sized outlet plenums. In the real world, however, broad turndown ranges, changing feedstock, incorrectly sized tube fields, and poorly designed plenums play havoc on separating liquid sulfur from the SRU process gas. PTI's Entrained Sulfur Removal Elements - ESRE™ and Heated ESRE™ solve these problems.

The modified-Claus sulfur recovery unit with supporting Tail Gas Treaters or Scrubbers is a highly efficient means to remove sulfur from process streams. At each stage of the process, the sulfur produced in the system is condensed and collected as molten liquid sulfur. The sulfur condenser, quite literally, is the most important component of a Sulfur Unit. Without it, the other equipment in the unit cannot operate efficiently.
Sulfur Condenser design is critical. Properly designed tube fields, with optimum mass velocities across all operating regimes, coupled with properly sized disengaging plenums allow the formed sulfur droplets to efficiently separate with little help from anything more than gravity.
Poorly designed condensers with inadequate sulfur separation can lead to fog or mist in sulfur condensers causing sulfur to lay out on cat beds and a high sulfur load in the TGTU, reducing your overall SRU Recovery Efficiency.
In the 25 years that PTI has supported sulfur unit operations, plus the additional decades of industry experience our sulfur experts have gathered, we have seen a handful of common condenser design problems.
- Oversized condenser tube fields provide ample heat transfer area but allow the formation of sulfur fog. Fog droplets that are so small the turbulence of the process gas stream prevents natural separation.
- Undersized sulfur plenums that simply do not provide adequate time for entrained sulfur droplets to reach terminal velocity and separate.
- Properly sized sulfur plenums that “short-circuit” the disengaging space due to external piping nozzle locations.
- Legacy units that were well designed a few decades ago but no longer operate at the original design feed rates and composition. Less sour feedstocks can swing your sulfur unit from H2S Rich to H2S Lean, moving your condenser design outside its original performance envelope.
Regardless of the reason, any newly formed liquid sulfur that is not captured in the condenser plenums passes to the next phase of the unit. In the case of your tail gas treater or flue gas scrubber, this sulfur is wasted as it is either converted back to hydrogen sulfide or consumed by caustic in the scrubber.
Properly designed condensers with adequate disengaging plenums can significantly reduce most of your sulfur carryover concerns. Undersized condenser plenums, units operating outside their original design envelope, and upset conditions may require a little extra help.
Woven mesh mist pads were commonly used in the ’70s and ’80s; however, most of these pads were ultimately removed and never replaced because they eventually plug causing an operational and maintenance headache.
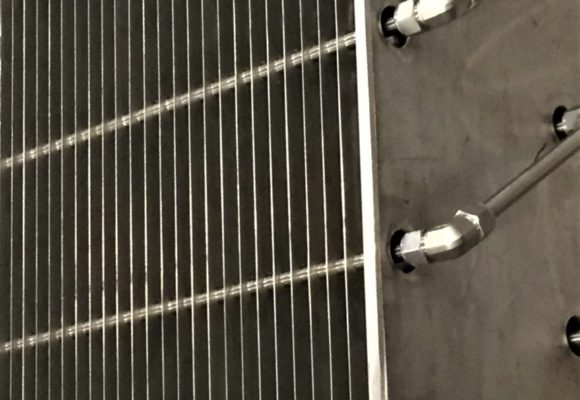
Parallel Plate coalescing vane separators are a great alternative to legacy mist pads used in sulfur condenser service. The recovery efficiency is comparable to mist pads but with a lower pressure drop. Plate separators drain vertically along smooth coalescing plates, which help wash away soot or ammonia salts that could build up in a mesh pad. Parallel plate elements also have a reduced surface area compared to mist pads which helps prevent liquid sulfur hold-up that ultimately will freeze during unit outages or significant upsets.
Our patented (US 9,313,829) ESRE™ plate separators incorporate a heated core into the separator design to heat soak the elements during unit shutdowns allowing additional time for any residual molten sulfur to drain from the system or re-melt frozen sulfur before start-up.
Properly sized Entrained Sulfur Removal Elements™ can improve overall SRU recovery efficiency and mitigate maintenance headaches and throughput losses due to high-pressure drops typically caused by clogged mist pads.
related Specialty Equipment


Amine Filtration Systems

Electric Process Gas Heaters for Sulfur Recovery Units

Hazardous Area Gas Monitoring
Low-Pressure Rich Amine Flash Drums (RAFD)
SRU Modified-Claus Process Burners

SRU Tail Gas Diverter Valves

Sulfur Complex Burner Management Systems

Sulfur Facility Process Safety and Control Systems

Sulfur Handling & Degassing


